Harness the Sun's Power: Your Guide to Understanding Solar Energy Basics
Solar Basics
Solar energy is a renewable and abundant source of power. By installing a solar electric system, you're essentially creating your own power station right at your home or business. At Sun City Solar Energy, we're committed to helping you understand and harness this powerful resource.
How Solar Electric Systems Work
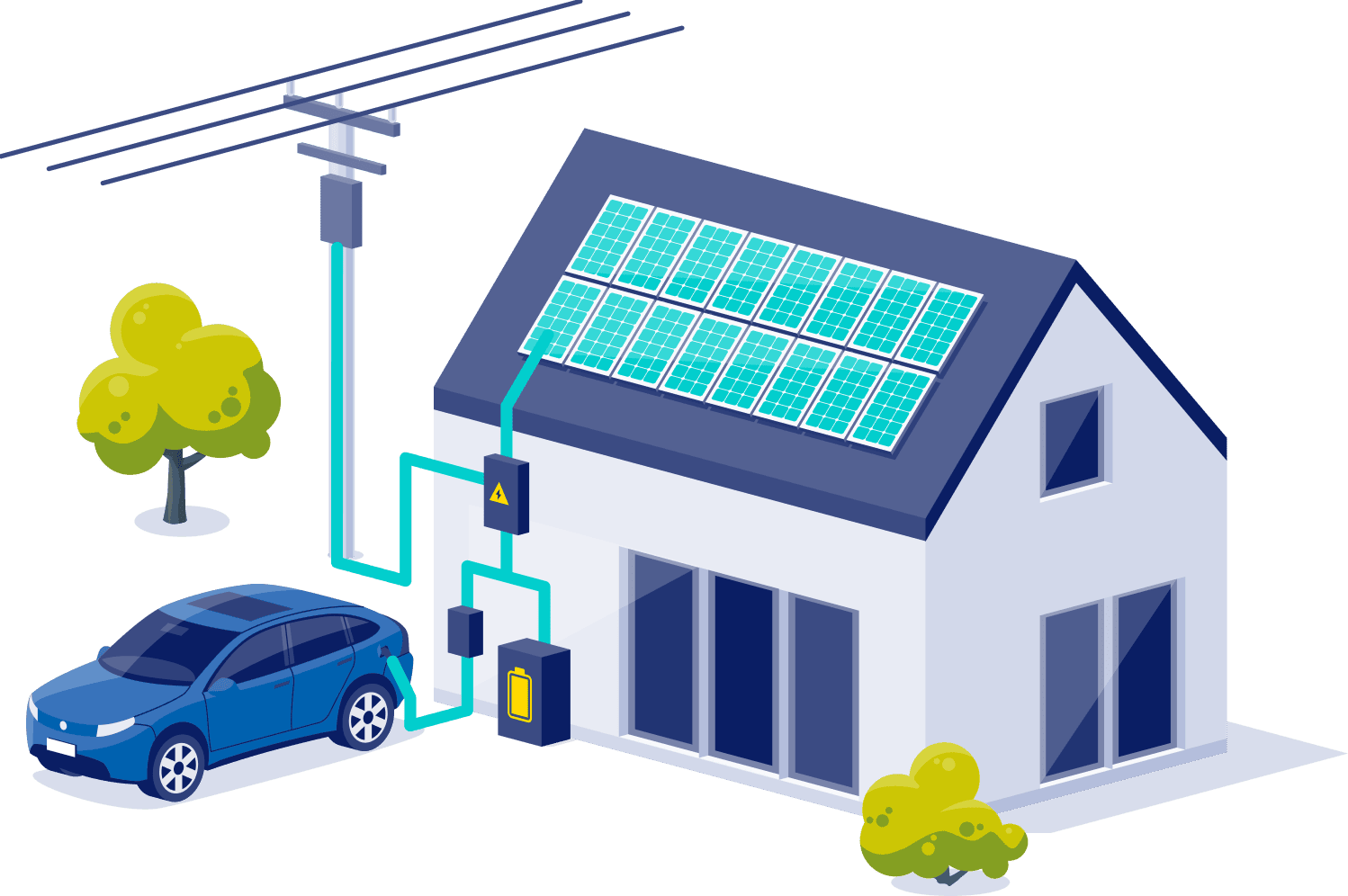
When sunlight hits the photovotaic panels installed on your property, it generates a flow of electrons. This is known as Direct Current (DC) electricity. An inverter changes this DC into Alternating Current (AC) electricity, which is the type of electricity that powers your home and appliances. In a grid system, excess electricity is sent to the main power grid an the customer receives a credit. In an off-grid system, excess electricity is stored in a battery for future use.
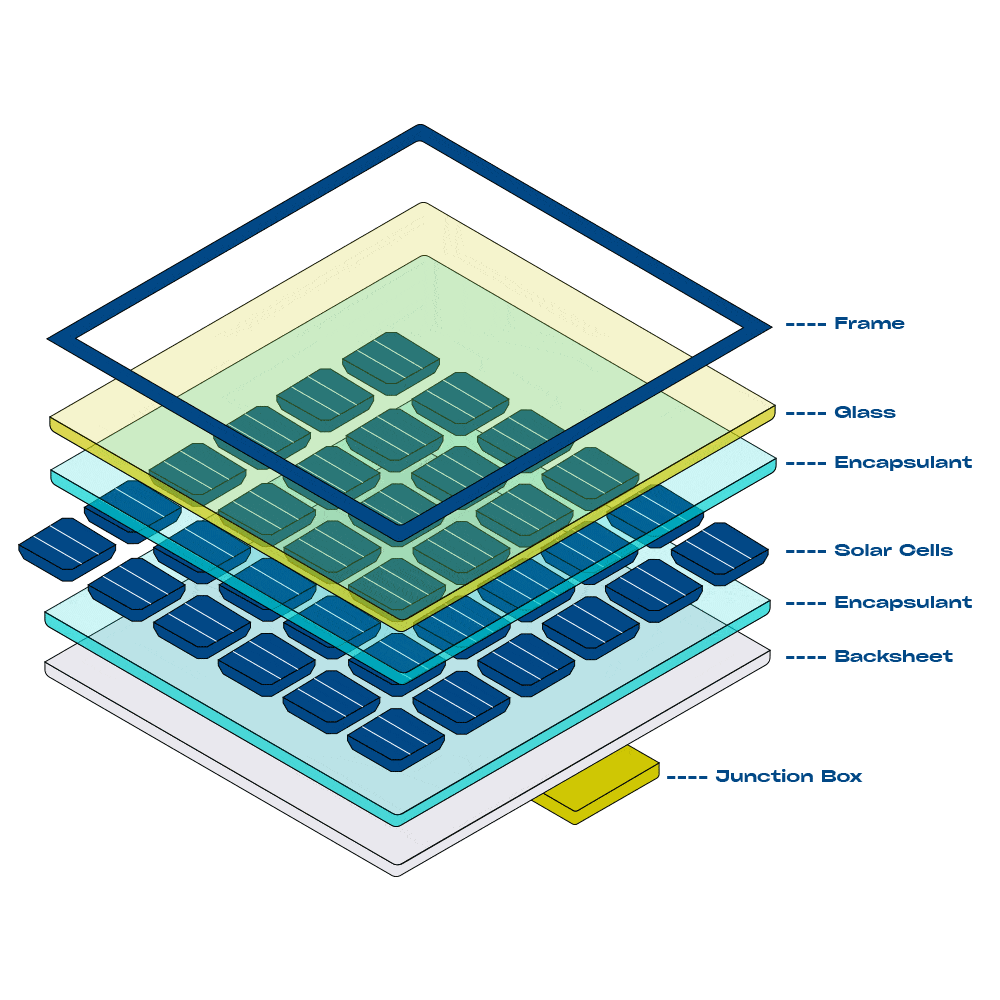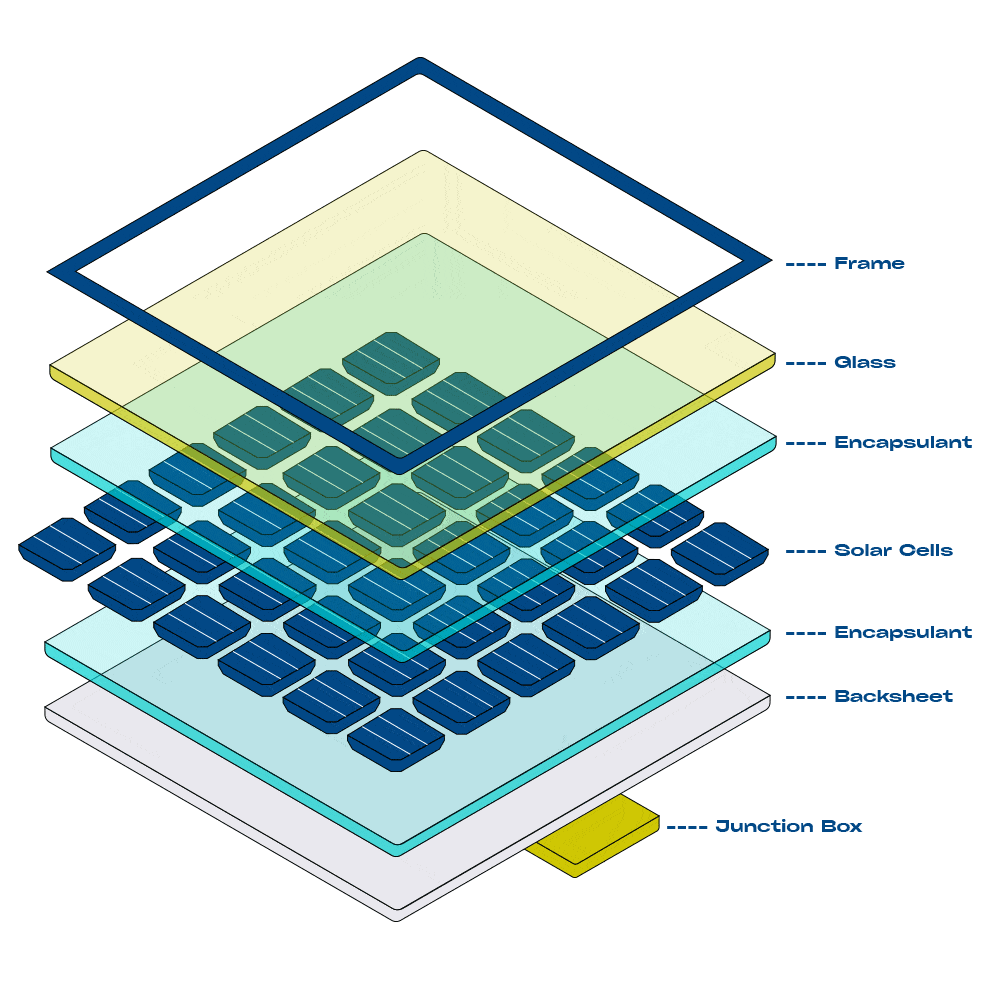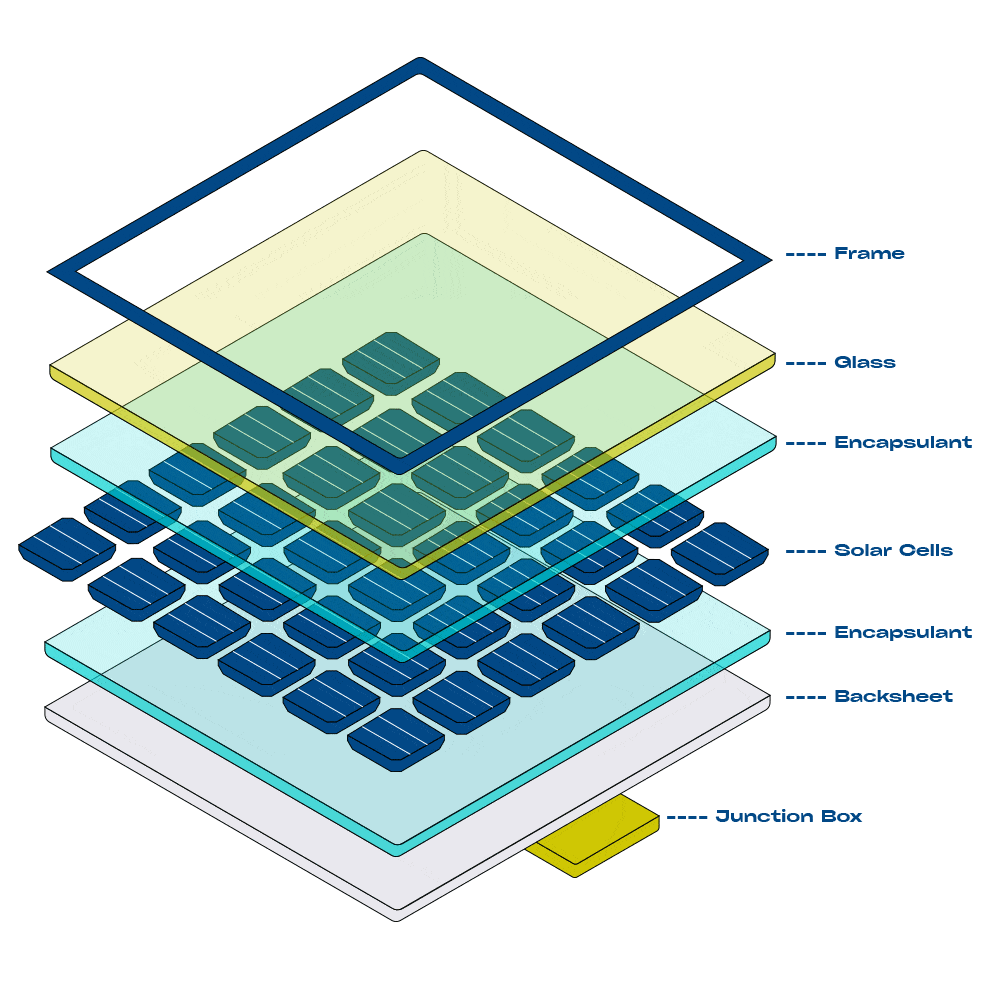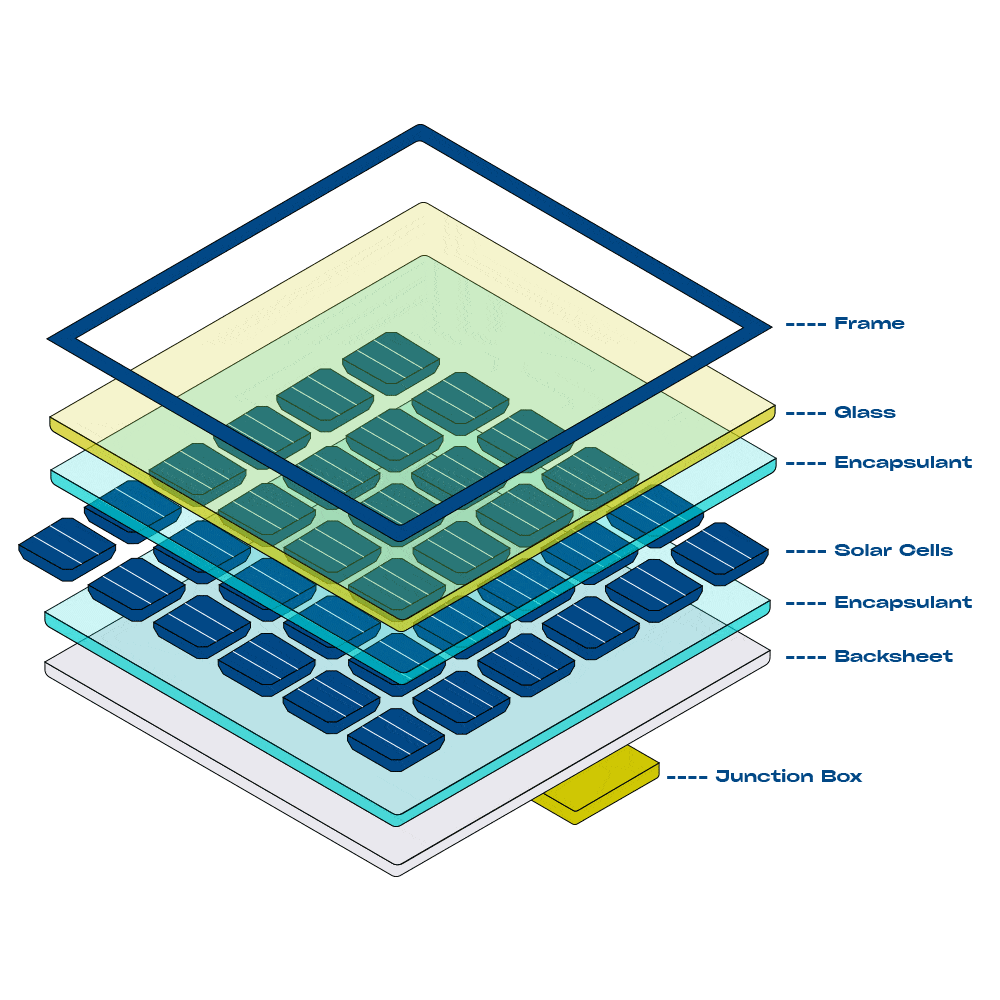
Components of a Solar System
Solar panels are made up of many photovoltaic cells wired together. These cells are typically made of Monocrystalline or Polycrystalline silicon. Monocrystalline cells are highly efficient at converting sunlight into electricity, while Polycrystalline cells are more cost-effective and produce less waste.
The inverter is a crucial component of any solar energy system. It converts the DC electricity produced by the solar panels into AC electricity, which is used in homes and businesses.
Transferring the Electricity
Several electrical components are required to transfer the electricity from the solar panels to your home or the utility grid. These include a utility-required disconnect and a back-feed breaker in your home's main electrical panel. All electrical work for Sun City Solar installations is completed by experienced and licensed electricians.
Monitoring Your Solar System
After the solar installation is complete, most utilities will install a special meter. This meter measures the power you consume from the grid and the power you send back to the grid from your solar system.
A monitoring system ensures your solar array is operating efficiently. It provides real-time information on your system and alerts you to any issues. Monitoring systems installed by Sun City Solar allows you to view detailed information on your system's performance through a smartphone app and a web-based site.

Choose Your Solar Solution

Residential

Commercial
How Photovoltaics Work
STEP 1
Sun shines on the photovoltaic modules and produces the flow of electrons known as Direct Current (DC) electricity.
STEP 2
DC electricity is fed into a solar inverter that inverts DC into Alternating Current (AC) electricity. AC electricity is used to power your home and all of your appliances.
STEP 3
The inverter is connected to your homes main electrical panel. If there is an immediate need for electricity while being produced, your home uses solar power directly.
STEP 4
STEP 5

Fundamentals Of Photovoltaics
Solar
Panels
Solar panels, often called solar modules, are typically made of many solar cells wired together. Photovoltaic cells are tile-sized silicone wafers, wired together and encased in protective glass and metal frame to create a module. They often have a blue or black appearance. Most solar modules installed today are either Monocrystalline or Polycrystalline.
Monocrystalline Photovoltaics
Polycrystalline Photovoltaics
Inverter
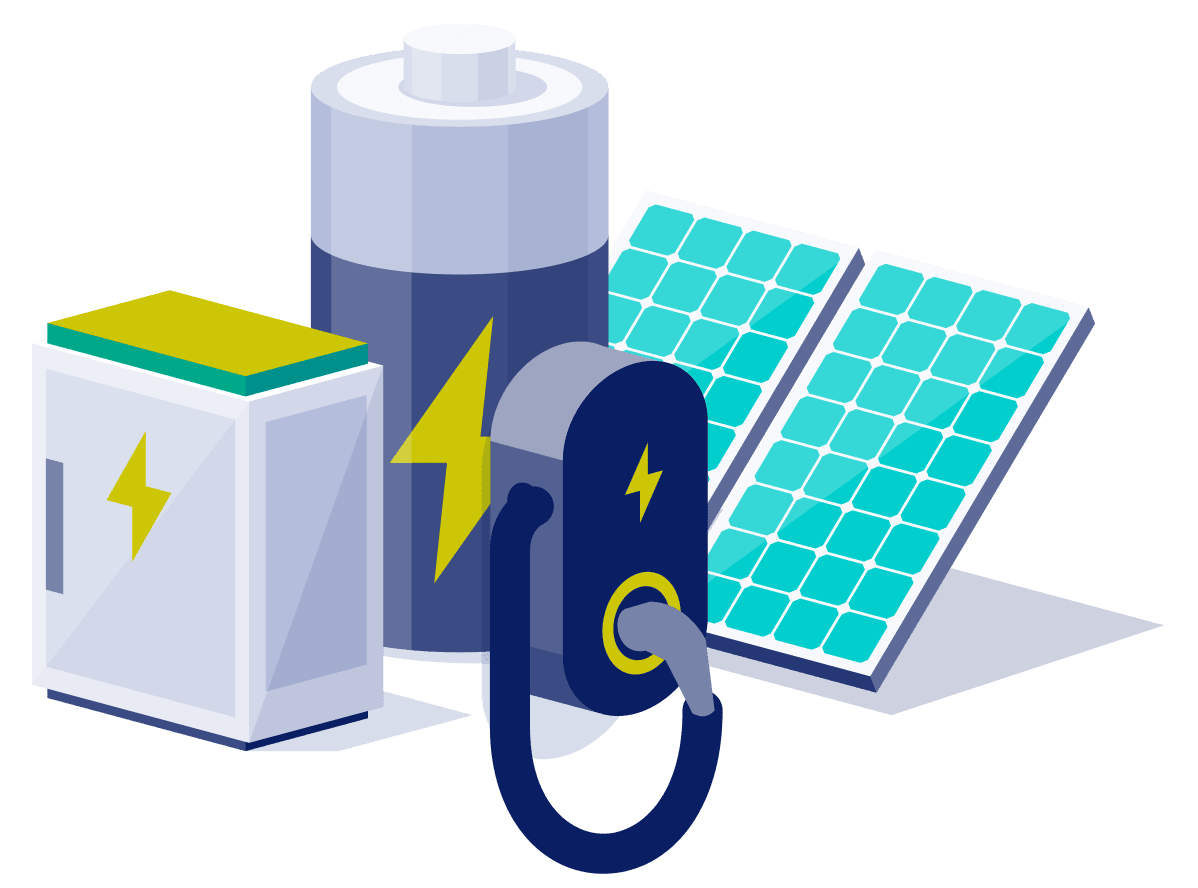
Types of Inverter
• Microinverter
• String Inverter
• Hybrid/Battery Based Inverter
Electrical (Panel, Disconnects)
To transfer the electricity produced from the Photovoltaic solar modules to the home to use or onto the utility grid requires installing several electrical components. After the energy is passed from the module and inverted to AC by the inverter, the power feeds into a utility-required disconnect. The disconnect is required by all utility companies and is installed near the utility meter. The disconnect allows the utility to shut down the solar system at any time so work can be performed on the main power lines without the system feeding energy onto the grid.
The solar electricity is routed to a back-feed breaker in the home’s main electrical panel from the disconnect. This allows the home to use the solar energy produced to run the current energy needs of the home. If the home needs more power than the solar can produce, the additional power is consumed from the grid and the solar power. If excess power is generated over the home’s current needs, the excess power is fed back onto the utility power grid and used by others. In states with net metering, this excess energy can be credited to the home’s electric bill.
For states without net metering, the excess energy produced can be fed into a battery backup system and stored for future use.
Utility Smart Meter
Monitoring System
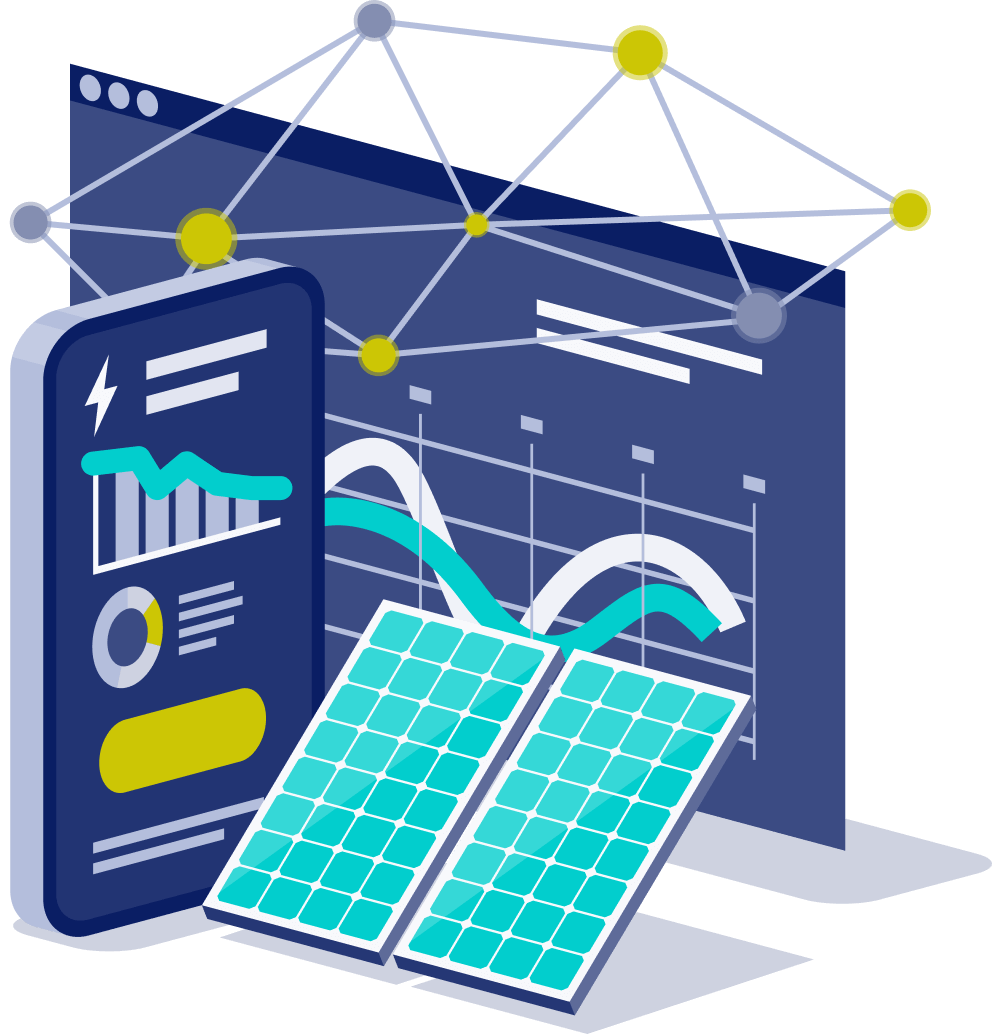
Monitoring systems installed by Sun City Solar allow a solar owner to have detailed real-time information on their system through both a smartphone app and a web-based site. Detailed information includes current energy production and detailed historical production on a daily/weekly/monthly basis.
To view the solar production details online, the monitoring system must be connected to the internet.
